Introduction
Survey of LLM inference systems
Basic computation graph of transformer model
- transformer
- prefill, decode
- kv cache
Inference engine:
- vLLM: Page Attention
- SGLang: Radix Attention
P/D disaggregated inference:
- Dynamo
KV Cache:
- Radix Attention
- LLMCache
- Mooncake
Model Parallelism:
- Tensor Parallelism
Kernel:
- MoE kernel
- Attention kernel
- Sparse attention
Engine
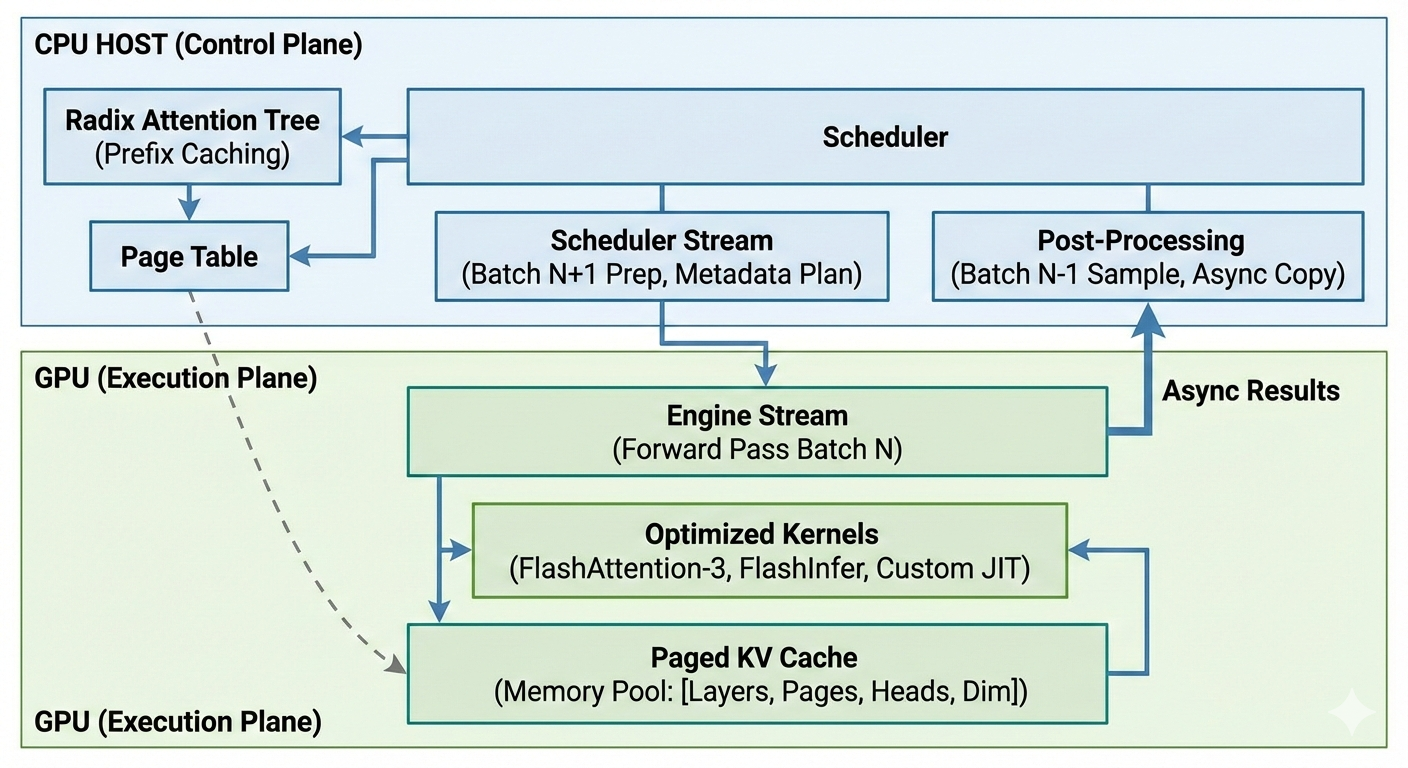
Paged KV Cache: The system manages GPU memory by dividing the Key-Value (KV) cache into fixed-size pages (blocks) rather than contiguous memory.Storage Layout: Memory is pre-allocated as a large tensor (e.g., [2, layers, pages, heads, dim]).Eliminating Fragmentation: By using a Page Table, the server can map non-contiguous physical memory pages to a logical sequence, allowing it to handle variable-length requests without wasting space.Vectorized Ops: Custom JIT CUDA kernels handle the writing of new tokens into these pages using warp-level vectorized memory operations to achieve peak bandwidth.
Radix Attention Tree (Prefix Caching): SGLang uses a Radix Tree structure to manage the KV cache and enable prefix caching.Prefix Matching: When a new request arrives (e.g., a prompt with a system message), the scheduler searches the Radix Tree for existing prefixes already stored in the KV cache.Computation Reuse: If a match is found, the server reuses the cached KV tensors, skipping the “prefill” phase for that part of the prompt, which significantly reduces latency and GPU load.LRU Eviction: When GPU memory is full, the system uses a Least Recently Used (LRU) policy to evict old tree nodes (and their corresponding physical pages).
Scheduler for Overlapping Computation: The “Overlap Scheduling” mechanism hides CPU overhead by pipelining CPU and GPU tasks using dual CUDA streams.The Problem: Normally, the GPU sits idle while the CPU schedules the next batch or processes the current result.The Solution: SGLang overlaps these tasks:GPU Task: The Engine Stream executes the model forward pass for Batch $N$.CPU Task: Simultaneously, the Scheduler Stream prepares metadata/memory planning for Batch $N+1$ and processes the results (sampling) of Batch $N-1$.Async Results: Token results are copied from GPU to CPU using pinned memory and non-blocking transfers, ensuring the GPU never waits for the CPU to catch up.
全面剖析推理框架技术原理: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/b_4YhTa96Zeklh23lv8qBw
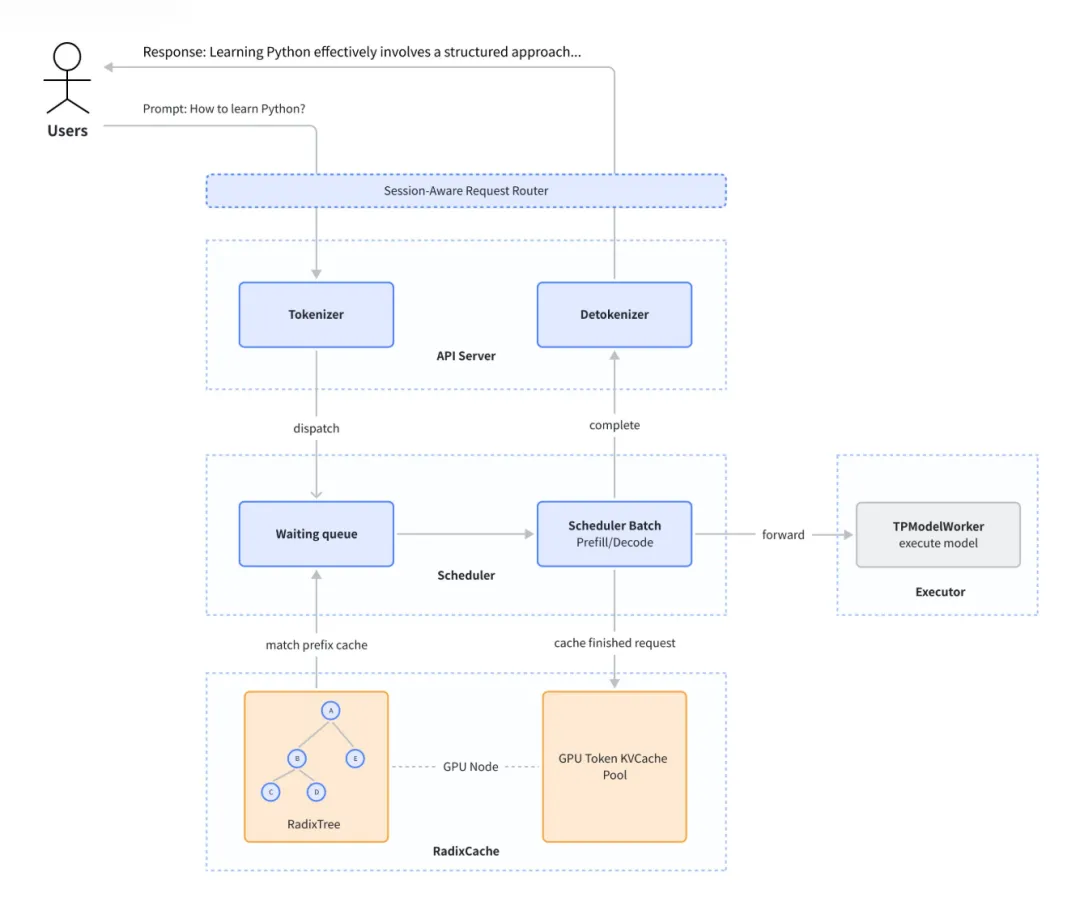
SGLang 的整体架构很清晰,从请求执行流程来看,大致能分为服务接口层、调度层和执行层:
服务接口层(Serving Interface):核心组件有 API Server、Tokenizer(分词器)、Detokenizer(去分词器),主要负责接收请求、下发请求,以及处理简单的编解码逻辑。
调度层(Scheduler):核心是 Scheduler 类,它集成了组 Batch 策略(Scheduler Policy)、Disaggregation(PD 分离)、Overlap 以及输出处理等特性(以 Mixin 方式嵌入,代码文件是独立的);Radix Cache(前缀 KV 缓存管理)、Prefill Adder(请求组 Batch)等功能模块是单独实现的。
执行层(Executor):以 TPWorker 作为核心入口,接收调度层的指令,支持张量并行(TP)和流水线并行(PP)。TPWorker 会协同管理 Model Runner,集成了多种计算后端、 Memory Pool 和 NCCL Group(通信组),一起完成模型推理计算。
其简化的请求流程如下图所示:
Kernel
Attention: FA-3, FlashInfer
Kernel Fusion: just-in-time (JIT) compiled kernel for better runtime performance.